Lab Report: Ointment
Effect of Different Ingredients on the Characteristics of an Ointment
Date of Experiment: 22nd April 2013
Lecturer’s Name: Dr. Haliza Katas
Aim: To study the effects of different ointment composition on the physical characteristics of ointment formed and the rate of drug released from it.
Introduction:
Ointment formulation is a semisolid dosage form which is suitable for external application on skin. It is oily preparations that contain one or more active ingredients that is soluble or spread homogenously. A good ointment must have an appealing texture, easy to use on skin characteristic as well as releasing it active ingredient from it.
Generally, ointment composed of active ingredient either powder or liquid that is incorporated into the oily semisolid continuous phase. In Pharmaceutics, ointment preparation is used to act as local treatment at application site, increasing the moisture of the skin (emollient effect).
Apparatus:
Weighing balance 2 Threads
Weighing boat Glass rod
100ml beaker Water Bath
Heater Pipette
Glass slab & spatula Plastic Kuvette
Mortar & pestle UV spectrophotometer
Dialysis bag (10cm)
Materials:
Emulsifying wax Acetylsalicylic acid
White soft paraffin Distilled water
Liquid paraffin
Procedure:
1. Emulsifying ointment (50g) is prepared using the formula below:
|
Emulsifying Ointment |
Group |
Materials (g) |
Total (g) |
||
|
Emulsifying wax |
White Soft Paraffin |
Liquid Paraffin |
|||
|
I |
1,5 |
21 |
25 |
4 |
50 |
|
II |
2,6 |
17 |
25 |
8 |
50 |
|
III |
3,7 |
13 |
25 |
12 |
50 |
|
IV |
4,8 |
9 |
25 |
16 |
50 |
2. 5g of ointment formed is taken out and put into the weighing boat and it is then labelled. The texture, clarity, colour of ointment, spreadibility, greasiness, and hardness of the ointment is explained and compared.
3. 1.5g Acetylsalicylic acid powder is incorporated into the 15g ointment prepared by using levigation technique. If necessary, the acetylsalicylic acid is first mashed into fine powders by using mortar and pestle.
4. The acetylsalicylic acid ointment is put into dialysis beg and both end of the bag were tied up neatly.
5. The bag consisting acetylsalicylic acid ointment is put into 250ml beaker containing 100ml distilled water that has been heated to 37ºC.
6. At time interval of 5 minutes, 3-4ml aliquot sample is pipette and the release of acetylsalicylic acid from the ointment base is determined by using UV spectrophotometer. Ensure that the distilled water is mixed by using glass rod before taking out the sample.
Results and Discussion:
1. Comparison of the physical appearance of the each ointment.
| Group | Texture | Clarity | Colour | Greasiness | Spreadability |
| Emulsifying Ointment V | Hardest | Higly Opaque | White | Least greasy | Very difficult |
| Emulsifying Ointment VI | Hard | Opaque | White | Less greasy | Difficult |
| Emulsifying Ointment VII | Soft | Clear | White | Greasy | Less Difficult |
| Emulsifying Ointment VIII | Softest | Very Clear | White | Very greasy | Easily |
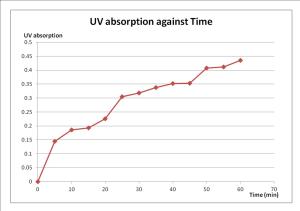
2. Plot UV absorption graph against time. Give explanation.
From this experiment, distilled water in the beaker represents the blood circulation in the body. Since distilled water is hypotonic so acetylsalicylic acid inside the dialysis bag can diffuse out from the dialysis bag. Hence, acetylsalicylic acid will diffuse out to the hypotonic solution against concentration gradient. As a result, the content of acetylsalicylic acid in the distilled water increases. Dialysis bag acted as phospholipid bilayer and this experiment is conducted in 37ºC because the temperature mimics human body temperature. The UV absorption value obtained from the spectrophotometer represents the amount of acetylsalicylic acid released from the ointment into the distilled water through the dialysis beg.
Based on the graph above, it shows that the UV absorption value increases with time. This means that amount of acetylsalicylic acid in the distilled water increases with time. The gradient of the graph represents the rate of drug (acetylsalicylic acid) release to the blood circulation (distilled water). The gradient or rate of acetylsalicylic acid release is not consistent, some is steeper but some is less steep. When the gradient is low or at the less steep part, the distilled water that pipetted out for the test in spectrophotometer is saturated. This is because it is not stir evenly before taking out the sample. When the UV absorption value increases, the acetylsalicylic acid release from the dialysis bag into the surrounding solution also increases. If the saturation occurred, the graph become constant and the rate of release becomes nearly zero because the concentration of acetylsalicylic acid in the distilled water is isotonic to the concentration of ointment.
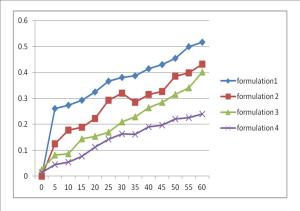
3. Plot a graph of UV absorption against time for the ointment preparation that contain different composition. Compare and discuss the result.
|
Time (min) |
Average of UV absorption at 300nm (x+ SD) |
|||||||||||||
|
0 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
40 |
45 |
50 |
55 |
60 |
||
|
Emulsifying Ointment I |
Group 1 |
0 |
0.423 |
0.443 |
0.464 |
0.521 |
0.579 |
0.586 |
0.591 |
0.636 |
0.648 |
0.655 |
0.730 |
0.738 |
|
Group 5 |
0 |
0.098 |
0.105 |
0.120 |
0.127 |
0.153 |
0.175 |
0.183 |
0.192 |
0.214 |
0.255 |
0.271 |
0.296 |
|
|
Average(x) |
0 |
0.261 |
0.274 |
0.292 |
0.324 |
0.366 |
0.381 |
0.387 |
0.414 |
0.431 |
0.455 |
0.500 |
0.517 |
|
|
SD |
0 |
0.163 |
0.169 |
0.172 |
0.197 |
0.213 |
0.206 |
0.204 |
0.222 |
0.343 |
0.200 |
0.229 |
0.221 |
|
| Emulsifying Ointment II |
Group 2 |
0 |
0.104 |
0.168 |
0.183 |
0.219 |
0.278 |
0.321 |
0.237 |
0.278 |
0.300 |
0.362 |
0.383 |
0.428 |
|
Group 6 |
0 |
0.145 |
0.186 |
0.193 |
0.226 |
0.305 |
0.318 |
0.338 |
0.352 |
0.353 |
0.407 |
0.412 |
0.435 |
|
|
Average(x) |
0 |
0.125 |
0.177 |
0.188 |
0.223 |
0.292 |
0.320 |
0.284 |
0.315 |
0.327 |
0.385 |
0.398 |
0.432 |
|
|
SD |
0 |
0.021 |
0.009 |
0.005 |
0.004 |
0.014 |
0.002 |
0.051 |
0.037 |
0.027 |
0.023 |
0.015 |
0.004 |
|
|
Emulsifying Ointment III |
Group 3 |
0 |
0.047 |
0.049 |
0.146 |
0.158 |
0.183 |
0.220 |
0.236 |
0.253 |
0.277 |
0.289 |
0.319 |
0.387 |
|
Group 7 |
0.052 |
0.114 |
0.122 |
0.141 |
0.150 |
0.154 |
0.200 |
0.220 |
0.274 |
0.293 | 0.341 | 0.360 |
0.417 |
|
|
Average(x) |
0.026 |
0.081 |
0.086 |
0.144 |
0.154 |
0.169 |
0.210 |
0.228 |
0.264 |
0.285 |
0.315 |
0.340 |
0.402 |
|
|
SD |
0.026 |
0.034 |
0.037 |
0.003 |
0.004 |
0.015 |
0.010 |
0.008 |
0.011 |
0.008 |
0.026 |
0.021 |
0.015 |
|
| Emulsifying Ointment IV |
Group 4 |
0.028 |
0.051 |
0.068 |
0.086 |
0.140 |
0.175 |
0.204 |
0.183 |
0.205 |
0.214 |
0.215 |
0.206 |
0.230 |
|
Group 8 |
0 |
0.036 |
0.040 |
0.065 |
0.082 |
0.109 |
0.122 |
0.141 |
0.177 |
0.180 |
0.225 |
0.246 |
0.250 |
|
|
Average(x) |
0.014 |
0.044 |
0.054 |
0.076 |
0.111 |
0.142 |
0.163 |
0.162 |
0.191 |
0.197 |
0.220 |
0.226 |
0.240 |
|
|
SD |
0.014 |
0.008 |
0.014 |
0.011 |
0.029 |
0.033 |
0.041 |
0.021 |
0.014 |
0.017 |
0.005 |
0.020 |
0.010 | |
Ultraviolet spectrometer or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in ultraviolet-visible spectral region. It allows particle size distributions to be measured in concentrated systems without dilution. By using this technique, a light is passed through the sample that we are going to measure. When light travels through the sample, it loses energy, also known as attenuated. Therefore, if the sample contains the suspended particles, the attenuation of light will change due to a variety of scattering and absorption patterns. The changes of energy of the light are then be measured to indicate the size distributions of the particles in the sample.
Dialysis tubing is actually a semi-permeable membrane when it is used in water. It is made up from regenerated cellulose. Dialysis tube has been used in the experiment for illustrating osmosis and pressure gradients across a membrane. As it is semi-permeable, therefore it only allows certain molecules to pass through by diffusion and it will block some molecules such as polar compound to pass through the membrane. Diffusion is the movement of particle from the region of high concentration to the region of low concentration until equilibrium is reached.
In the experiment, dialysis tube had been use to determine the ability of the acetylsalicylic acid of ointment to pass through the membrane and enter into the water. The amount of the sample that passed through the dialysis tube is measured by using the ultraviolet spectrophotometry. Dialysis tube indicates the human’s skin. Based on the results, we can see that UV absorption at 300 nm is increasing with time for each of the ointments. Increasing in UV absorption indicates that there is increasing in the numbers of particle of the ointment diffuse through the dialysis tube membrane.
From figure 1, it was observed that the highest UV absorption is emulsifying ointment I and it is followed with the emulsifying ointment II and emulsifying ointment III. While emulsifying ointment IV has the lowest average UV absorbance. The higher the average UV absorbance, the higher the penetration rate of the drug from the dialysis tube and vice versa. Therefore, emulsifying ointment I that has the highest average UV absorption can indicate that it has the highest diffusion of the acetylsalicylic acid through the dialysis tube.
The variation in the penetration rate of the drug through the dialysis tube may be the amount of emulsifying wax and liquid paraffin (oil phase). Emulsifying wax influence the capability of ointment to hold water. Emulsifying wax will prolonged the the contact of ointment with the dialysis tube membrane which will lead to the formation of occlusive layer. The higher the amounts of emulsifying wax in the formulation, the greater the capability of the ointment to hold water. However, liquid paraffin that increasing amount of liquid paraffin led to a retardation of drug release from formulation. This is because increasing liquid paraffin may decrease the thermodynamic activity of the drug which can be expressed in term of relative solubility of the drug. This leads to the retardation of drug release from the ointment base.
Four emulsifying ointments that prepared in the experiment are made up of different proportion of the emulsifying wax and liquid paraffin. Ointment I has the most amount of the emulsifying wax and the least amount of liquid paraffin, therefore the acetylsalicylic acid is more efficient in penetration of the dialysis tube and has the highest average UV absorption. However, ointment IV has the least amount of the emulsifying wax and the highest amount of the liquid paraffin. Therefore, the salicylic is more difficult to penetrate the dialysis tube membrane and resulted with the lowest average UV absorption.
4. What is the function of each ingredient that is used in the ointment? How the different composition of the emulsifying wax and liquid paraffin affects the physical properties of the ointment and the release rate of a drug from it?
Emulsifying wax acts as an emulsifying agent which decreases the interfacial surface tension so that the drug particles can be distributed uniformly in the ointment and to prevent any sedimentation from occurring.
White soft paraffin is an ointment base which are used as an emollient and moisturizer. To increases the greasiness of the ointment so that it can penetrate through the skin hydrophobic lipid bilayer more easily.
Liquid paraffin acts as the base too. It softens the ointment formed. It also decreases the ointment viscosity and acts as emollient.
When the proportion of the emulsifying wax decreases and liquid paraffin increases, the spreadibility and greasiness of the ointment increase while the hardness decreases and thus the drugs can be released from the formulation and penetrate through the skin lipid bilayer more readily. Therefore, the rate of release of drug increases. However, this is different from results of formulation IV which may be due to the experiment errors such as the distilled water is not stirred before sampling. So, ideally, the formulation IV should have the highest rate of release.
Conclusion:
Different composition of the ointment can affect the physical properties of the ointment formed and also the rate of release of the drug from the formulation. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the components of the formulation are in suitable proportion to produce a drug formulation which has desired therapeutic effects.
References:
1. Aulton, M.E. 1998. Pharmaceutics: The science of dosage form design. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.